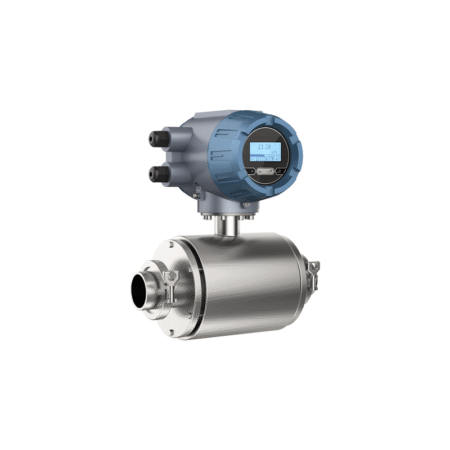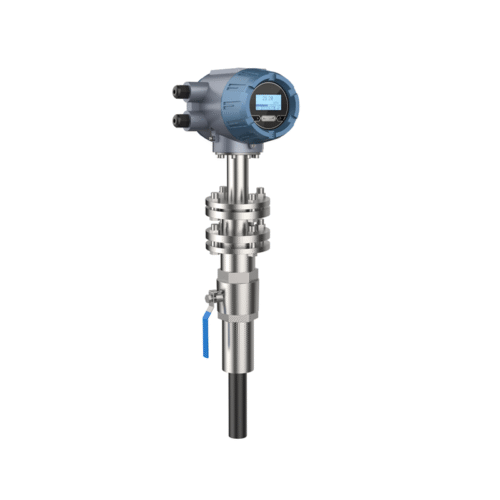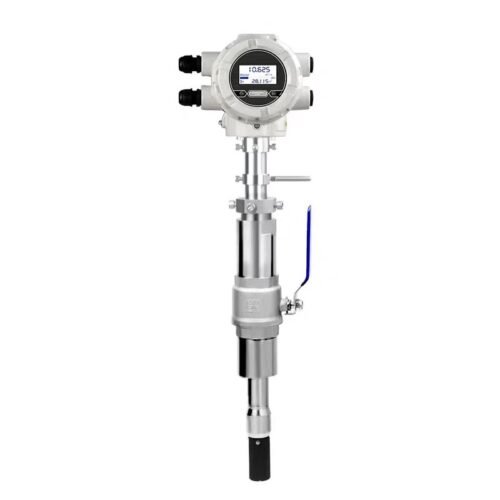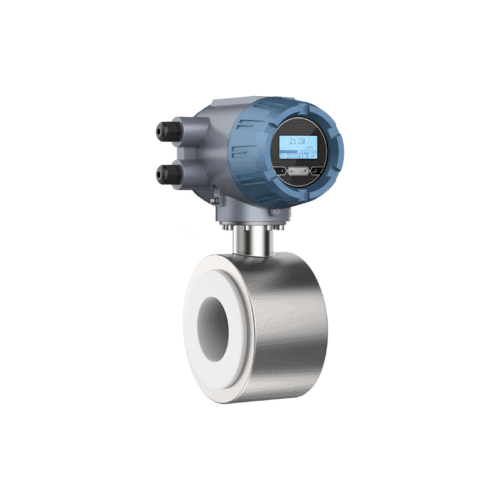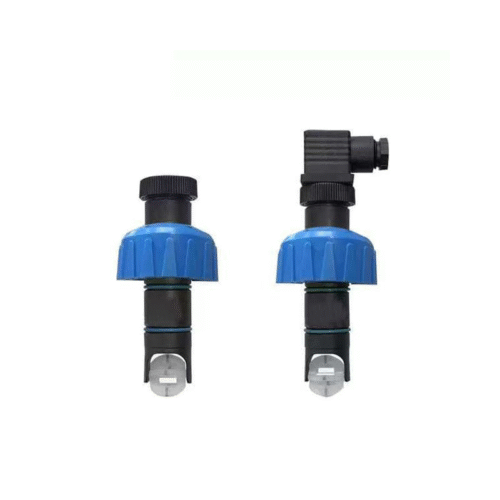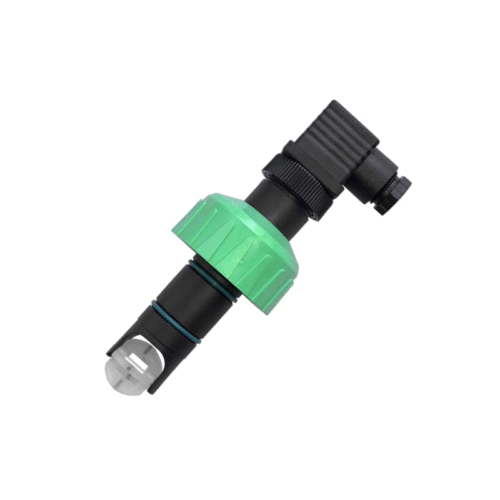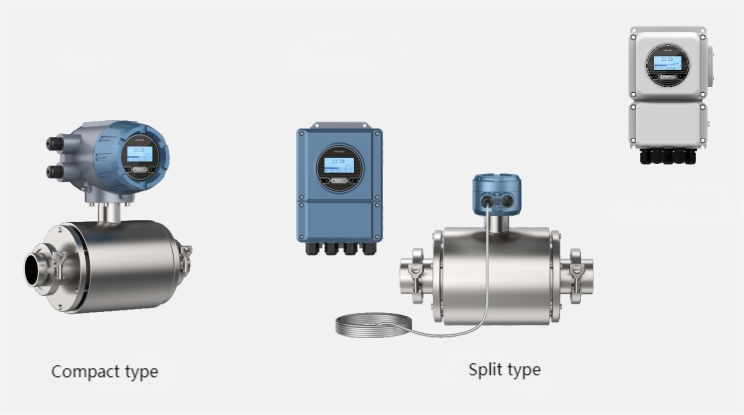
The tri-clamp type electromagnetic flow meter is also designed and manufactured based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. Its components and functions are identical to those of the flange-type electromagnetic flowmeter. However, it utilizes a clamp-type quick-connect connection, making it suitable for hygienic applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food. This facilitates frequent meter disassembly for cleaning, ensuring pipeline hygiene. The sensor housing is constructed entirely of stainless steel, meeting the 3A hygiene standards of the food industry.
Principle
According to Faraday’s principle of electromagnetic induction, a pair of detection electrodes is installed on the tube wall perpendicular to the axis of the measuring tube and the magnetic field lines. When the conductive liquid moves along the axis of the measuring tube, it cuts the magnetic field lines and generates an induced potential. This induced potential is detected by the two detection electrodes, and the value is proportional to the flow rate. Its value is
Its value is
E=KBVD
In the formula:
E-induced potential;
K-Coefficient related to magnetic field distribution and axial length;
B-Magnetic induction intensity;
V-average flow velocity of conductive liquid;
D-electrode spacing;(Measuring the inner diameter of the tube).
The sensor uses the induced potential E as a flow signal, which is transmitted to the converter. After amplification, transformation, filtering, and a series of digital processing, the instantaneous and cumulative flow rates are displayed on a back-lit dot matrix LCD. The converter has 4-20mA output, alarm output, and frequency output, and is equipped with communication interfaces such as RS-485, and supports HART and MODBUS protocols.